Introduction to Speech Therapy for Stuttering
Stuttering is a speech disorder that can create significant challenges for individuals in expressing themselves fluently. Fortunately, speech therapy offers a structured path to help people overcome these hurdles. In this article, we’ll explore the techniques, benefits, and methods of speech therapy for stuttering, along with tips for families and caregivers who want to provide support.
Understanding Stuttering
What Is Stuttering?
Stuttering, also known as stammering, is a condition that affects speech flow. It often involves repetitions, prolongations, or blocks when trying to speak. These disruptions can vary in severity and may be accompanied by physical symptoms like facial tension or rapid eye blinking.
Common Causes of Stuttering
Stuttering can stem from various factors, including genetics, neurological differences, or developmental delays. While there’s no single cause, a combination of genetic and environmental influences often plays a role in its onset.

Importance of Speech Therapy
How Speech Therapy Helps
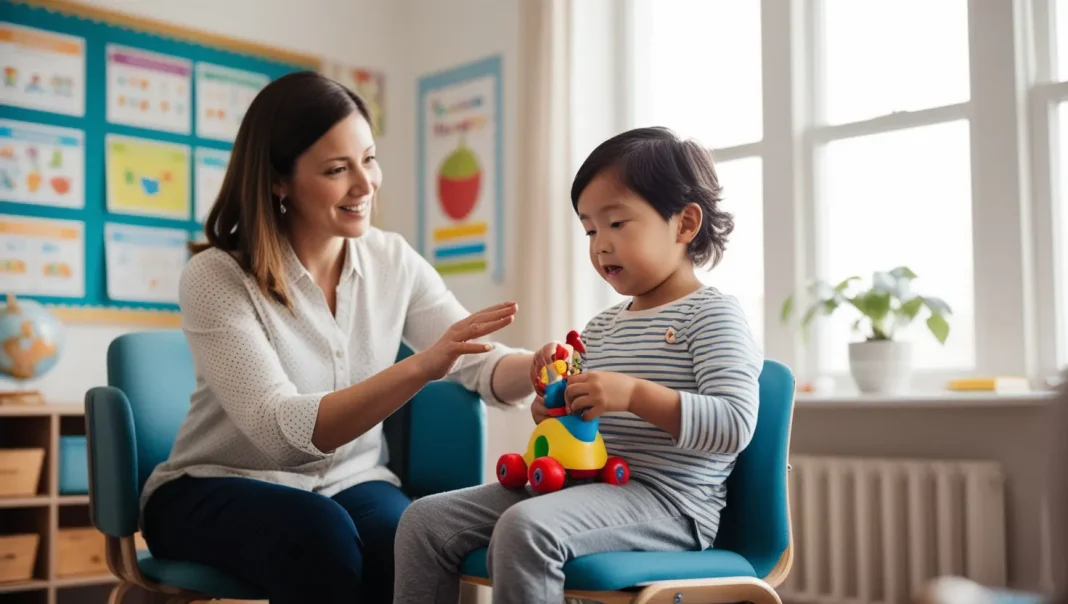
Speech therapy provides a safe and supportive environment for individuals to practice techniques that enhance fluency. By working with a trained therapist, those who stutter can learn ways to control their speech, reduce tension, and communicate more confidently.
Key Goals of Therapy
The primary goals in stuttering therapy are to reduce speech interruptions, increase fluency, and boost self-esteem. Therapy is not a quick fix but rather a long-term strategy to help individuals gain control over their speech.
Techniques Used in Speech Therapy
Breathing Exercises
Effective breathing techniques can be beneficial for those who stutter. These exercises focus on helping individuals control their airflow, which is crucial for smooth speech.
Diaphragmatic Breathing
Diaphragmatic breathing involves using the diaphragm for deeper breathing. This technique helps relax the vocal cords and enables smoother speech.
Timed Breathing
Timed breathing exercises, where the individual practices inhaling and exhaling rhythmically, help in pacing speech and reducing speech anxiety.

Slow and Deliberate Speech
Speaking slowly and carefully allows those who stutter to focus on each word, reducing the likelihood of interruptions. This approach is often one of the first techniques taught in therapy sessions.
Fluency Shaping Therapy
Rate Control
Rate control involves slowing down the rate of speech, giving the speaker more time to focus on their words and easing any anxiety.
Smooth Transitions
Practicing smooth transitions between words and sentences helps reduce blocks and hesitations in speech.
Behavioral Strategies
Positive Reinforcement
Positive reinforcement encourages the speaker to keep working on their speech through rewards and praise. It’s especially effective for children who stutter.
Self-Monitoring
Self-monitoring helps individuals become aware of their speech patterns and make adjustments as they speak. This practice promotes self-awareness and gradual improvement.
Cognitive Approaches
Addressing Anxiety
Anxiety often exacerbates stuttering, so managing it is a crucial part of therapy. Techniques like visualization and relaxation can reduce the nervousness that contributes to stuttering episodes.
Building Confidence
Confidence-building exercises, such as public speaking practice in small groups, can help individuals feel more comfortable and less self-conscious about their speech.

Tips for Parents and Caregivers
Creating a Supportive Environment
Parents and caregivers play a vital role in helping someone who stutters feel comfortable and supported. Patience and encouragement can make a significant difference in a child’s progress.
Encouraging Communication
Rather than correcting or rushing the person, family members can encourage open, patient, and relaxed communication. This support can ease pressure and promote natural speaking.
When to Seek Professional Help
Signs That Therapy is Needed
While some stuttering may be developmental, if it persists or worsens over time, it might be a good idea to consult a speech therapist. Consistent blocks, physical tension, and growing frustration are signs to watch for.
Consulting with a Speech Therapist
A licensed speech therapist can assess the specific needs of the individual and tailor a therapy plan. Early intervention often leads to better outcomes.
Conclusion
Speech therapy for stuttering can significantly enhance the quality of life for those affected by the condition. Through a blend of techniques and support, individuals can learn to communicate more freely and confidently.
FAQs
Q1: How long does speech therapy for stuttering take? A: The duration varies based on individual needs, but consistent sessions over several months are common.
Q2: Is stuttering curable? A: While it may not have a complete “cure,” therapy can help manage and reduce symptoms effectively.
Q3: What age is ideal for starting speech therapy? A: Early intervention is beneficial, but people of any age can benefit from speech therapy.
Q4: Can stuttering be triggered by anxiety alone? A: Anxiety can worsen stuttering but is not typically the sole cause. It’s usually a combination of factors.
Q5: Are there exercises I can do at home for stuttering? A: Yes, breathing exercises, slow speech practice, and self-monitoring are helpful practices that can be done at home.