Introduction
Autism, also known as autism spectrum disorder (ASD), is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that affects how individuals interact, communicate, and perceive the world around them. It is often diagnosed in early childhood, making it crucial for parents and caregivers to be aware of the signs and seek early intervention. But how do you know if your child has autism? This article aims to provide you with valuable insights and information to help you recognize the signs, understand the diagnostic process, and discover ways to support your child’s development.
Understanding Autism
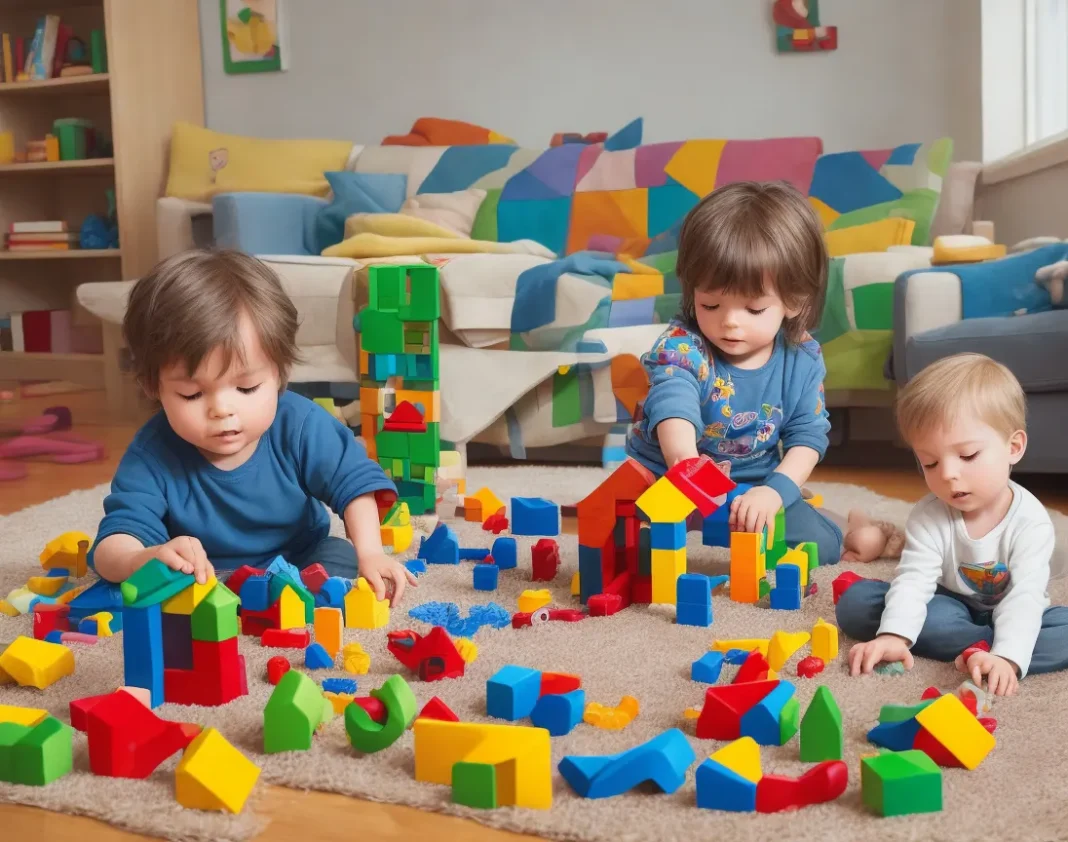
Autism is characterized by a wide range of symptoms and behaviors that can vary in severity. While each individual with autism is unique, there are common signs that parents can look out for. These signs typically manifest in the areas of communication, social interaction, and behavior.
Early Signs of Autism
One of the earliest signs of autism is a delay in or lack of communication skills. Children might not develop spoken language as expected, or they might have difficulty initiating or maintaining conversations. Additionally, repetitive behaviors and intense interests in specific subjects are often present. Children with autism might engage in repetitive body movements, show resistance to changes in routines, or exhibit intense focus on particular objects or topics.
Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of autism is paramount because it allows for timely intervention, which can significantly improve a child’s developmental trajectory. Research has shown that children who receive early intervention services exhibit better communication skills, cognitive abilities, and adaptive behaviors. Parents and caregivers play a pivotal role in observing their child’s behaviors and seeking professional evaluation if concerns arise.
Diagnostic Process
Diagnosing autism involves a comprehensive assessment by a team of medical professionals and specialists. The process includes evaluating a child’s social communication skills, behavior patterns, and developmental milestones. Various assessment tools and criteria, such as the DSM-5, are used to determine whether a child meets the criteria for an autism diagnosis.
Differentiating Autism from Developmental Delays
It’s important to differentiate autism from other developmental delays, as early intervention strategies can vary based on the specific challenges a child faces. Autism is characterized by distinct social communication differences and repetitive behaviors that set it apart from other conditions. A precise diagnosis ensures that the child receives the appropriate support and interventions tailored to their needs.
Support and Interventions
Children with autism benefit from a range of interventions and therapies designed to address their unique challenges. Behavioral therapies, such as Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), help develop essential skills and reduce challenging behaviors. Speech therapy aids in improving communication abilities, while occupational and physical therapies address sensory sensitivities and motor skills development.
Creating an Inclusive Environment
Fostering inclusivity and understanding in society is essential for supporting individuals with autism. Embracing neurodiversity involves creating environments where differences are accepted and celebrated. Educating peers, teachers, and community members about autism can promote empathy and reduce stigma.
Parental Concerns and Questions
Parents often have concerns and questions when their child receives an autism diagnosis. It’s normal to worry about the future and the best ways to support their child. Addressing these concerns with accurate information and connecting with support groups can provide parents with a sense of community and guidance.
Promoting Positive Development
While autism presents challenges, it’s essential to focus on the strengths and talents of children with autism. Nurturing their interests and helping them build social and communication skills can lead to positive outcomes. Encouraging interactions with peers and engaging in activities that align with their passions can boost their confidence and self-esteem.
Challenges Faced by Families
Families raising a child with autism often face unique challenges. Emotional strain, financial burdens, and the need for ongoing therapies and interventions can be overwhelming. Seeking assistance from support organizations, government programs, and local resources can alleviate some of these challenges.
Myths and Facts about Autism
There are many misconceptions surrounding autism. Addressing these myths with accurate information is vital for reducing stigma and increasing understanding. For example, while individuals with autism might have communication differences, they can still form meaningful connections and relationships.
The Journey of Acceptance
Accepting an autism diagnosis can be an emotional journey for families. It’s important to remember that every individual is valuable and capable of growth. Embracing neurodiversity means acknowledging the unique strengths and qualities that individuals with autism bring to the world.
Celebrating Progress and Achievements
As children with autism make progress in their development, it’s crucial to celebrate their achievements, no matter how small. These victories signify the hard work of both the child and their support network. Sharing success stories can inspire others and promote a more inclusive mindset.
Conclusion
Recognizing the signs of autism and seeking early intervention can make a significant difference in a child’s life. By understanding the characteristics of autism, differentiating it from other developmental issues, and providing appropriate support, parents and caregivers can help their children thrive. Embracing diversity, dispelling myths, and celebrating achievements contribute to a more inclusive and compassionate society where individuals with autism can reach their full potential.
FAQs
Can autism be diagnosed in infancy? Early signs of autism can often be observed in infancy, but a definitive diagnosis typically occurs after a child’s second birthday.
Are there any medical tests for diagnosing autism? Autism is diagnosed through comprehensive behavioral evaluations and observations rather than medical tests.
Is autism a lifelong condition? Yes, autism is a lifelong condition. However, with proper support and interventions, individuals with autism can make significant progress.
What is the role of Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA) in autism therapy? ABA is a widely used therapy that focuses on improving behaviors and developing skills through positive reinforcement and structured interventions.
How can schools create an inclusive environment for children with autism? Schools can promote inclusivity by providing sensory-friendly spaces, offering individualized education plans, and educating staff and students about autism.